-
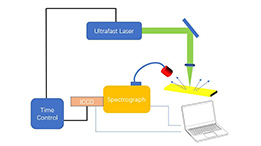
Zolix Spectrograph Application in LIBS
Laser induced break down(LIBS) is a method of analysis of materials. It is a kind of emission spectroscopy, very easy to analyse many kinds of elements at the same time. Since it was introduced for analytical field in 1962, especially in these two decades, LIBS has developed very fast. Now it has been researched not only in LABS, but in many field as well, such as metallurgy, cultural heritage and archaeology. Spectrograph also plays important role in LIBS system, despite of laser and fast detectors. -

Tunable Light Source-Uniform Light source
light sources are very popular in many optical experiments, but many can’t provide monochromatic light or a short bandwidth light. Tunable Light Source (TLS) can match these requirements. It’s very easy to achieve high bright emission light or hight resolution monochromatic light with a diffraction system. -
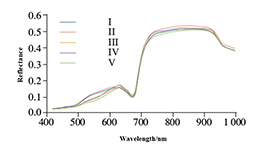
Maturity Detection of Camellia oleifera by Hyperspectral Imaging
Camellia oleifera fruits picking period is affected by environmental factors, different regions have different weather, climate, temperature, soil fertility and other conditions, resulting in early and late maturity of Camellia oleifera fruits, so the picking time of oil tea fruit should be based on its specific. Mature degree depends. The last month before harvesting is the peak period of oil accumulation, during which the oil content of the fruit increases most significantly, accompanied by the mutual transformation of internal nutrients. However, during this period, the external morphological characteristics of the fruit, such as shape and size, fresh fruit quality and color, tend to be stable and do not change significantly, which makes it difficult for tea farmers to determine the maturity of the fruit and the optimal harvesting period. Therefore, there is an urgent need to propose a rapid and accurate method to detect the maturity of Camellia oleifera fruits, which can help in the accurate harvesting operation of Camellia oleifera fruits. -
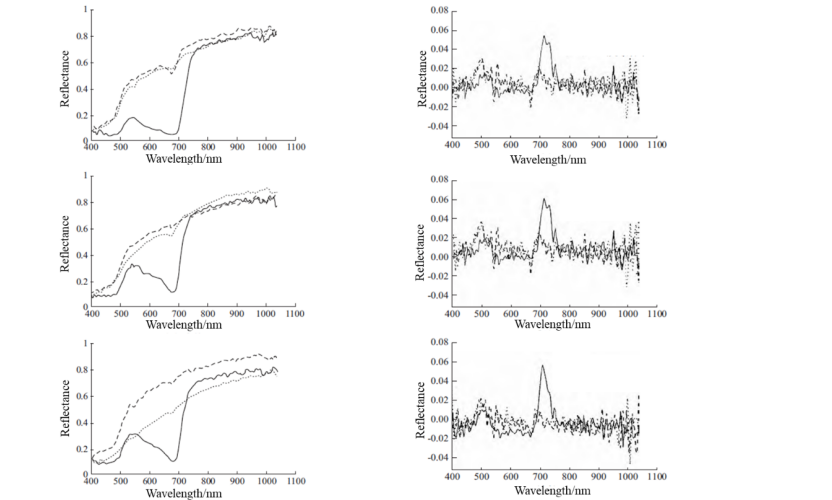
Estimation model of chlorophyll content of flue-cured tobacco based on hyperspectral
Chlorophyll is an important pigment for photosynthesis in green plants,affecting the exchange of material and energy between the crop and the outside world and the accumulation of material in the crop. The level of its content is an important indicator of the photosynthetic efficiency,developmental status and the roasting process of the plant, so the estimation of chlorophyll content in tobacco leaves is an effective means of monitoring the roasting status of roasted tobacco leaves. At the same time, there is a strong link between the chlorophyll content of crop leaves and the reflectance spectrum of the crop. Hyperspectral has the characteristics of multiple wavelength bands, unity of plot and high resolution, which fuse two-dimensional images and spectral techniques into three-dimensional mapping information. Chlorophyll detection by hyperspectral imaging is safe, fast, non-destructive and quantitative, and has great potential for the detection of chlorophyll content in large areas of leaves. -

GaiaSky-mini based monitoring of heavy metal contamination in agricultural soils
The application of GS spectroscopy can provide technical support for rapid monitoring and contamination evaluation of soil heavy metal content in agricultural fields on a large scale, and provide technical and theoretical support for further application of airborne or satellite-based hyperspectral remote sensing for quantitative monitoring of soil heavy metal contamination. There are still many objective factors that have yet to be resolved in the field monitoring of soil heavy metal content. When acquiring GS spectral data, the influence of meteorological conditions such as wind size, solar altitude angle, cloud limit or the particle size of the soil itself, the flatness of the soil surface, moisture content, etc. can affect the acquisition of spectral data
-
Products
Products
Photoelectric Test Systems
- SolarIV series Solar Cell Voltage and Current(IV)Characteristics Test System
- Sirius series Solar Simulator
- SCS600 series SolarCell Quantum Efficiency Measurement System
- SCS600-MAX Large Area Solar Measurement System
- DSR600 Photodetector Spectral Response Measurement System
- DSR300 Micro-nano Device Spectral Response Measurement System MORE >
Motorized Stages
- Motorized Linear Stages
- Motorized Vertical-Motion Stages
- Motorized Rotation Stages
- Motorized Goniometers
- Motorized Alignment Stages
- Custom Automation Equipment
Optical Breadboards
- OTSB Series Solid Aluminum Optical Breadboards, 13mm Thickness
- NTBB Series Stainless Steel Optical Breadboard, 50/100/150/200mm Thichness
- NTBP Series Stainless Steel Optical Breadboard, 50/100/150/200/300mm
- NTBR Series Stainless Steel Optical Breadboard, 50/100/150/200/300mm
- NTBK Series Honeycomb Optical Breadboards, 50/100/150/200/300mm
- Applications
- Technology
- Service
- Company
- Contact
- News